Global credit giant Visa has been researching smart contracts and programmable payments. The firm wants to let Ethereum holders set up automatic payments.
According to a proposal made public by Visa, Ethereum owners will be able to set up programmable payments using their own self-custodial wallets. The idea would also do away with banks and other centralized third parties from the transactions.
Automatic payments have been easy to set up on regular bank accounts. The technology and the money being moved are, however, ultimately in the jurisdiction of the bank. Visa is foraying into the world of self-custodied cryptocurrencies, and it is starting with Ethereum, which is the de facto standard.
In order to create a self-custodial wallet that can conduct automated recurring payments without requiring the user’s active participation, this method entails the construction of a smart contract that serves as an intermediary between a user account and a contract account.
Such a move would allow recurring payments to be conducted entirely over blockchain networks, which currently are devoid of such capability, Visa said. The company proposed deploying the solution on the Ethereum layer 2 network StarkNet.
What is Account Abstraction?
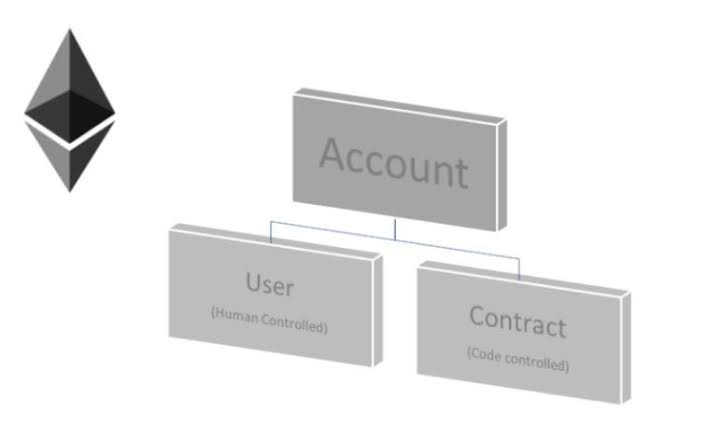
On the Ethereum network, there are currently two different kinds of accounts: Contract Accounts (CA), which are effectively smart contracts, and Externally Owned Accounts (EOA), which are managed by a private key.
Transactions can be started by EOAs, but not by CAs. According to Visa, it is feasible to establish a self-custodial wallet that can make recurring payments automatically by leveraging Account Abstraction to develop a smart contract that can perform transactions on behalf of an EOA.
On the Ethereum blockchain, Account Abstraction (AA) is a concept that tries to unify user accounts and smart contracts into a single type of account. This is made feasible by enabling the development of validity guidelines for specific transactions.
One use case of account abstraction is the development of “delegable accounts,” which enables the automation of payments through the use of smart contracts, is one use for AA.
According to Visa, a user can provide a pre-approved smart contract, known as an “auto payment contract,” the authority to start payments using a delegable account.
Here’s an example of how it may operate: The address of the auto payment contract is added to the user’s allow list if they visit a merchant’s website and consent to auto payments. As a result, the user’s account could begin a payment that would be legitimate since it was on the allow list by invoking the charge function of the auto payment contract, which the merchant could then use to activate a payment.


